
Menu
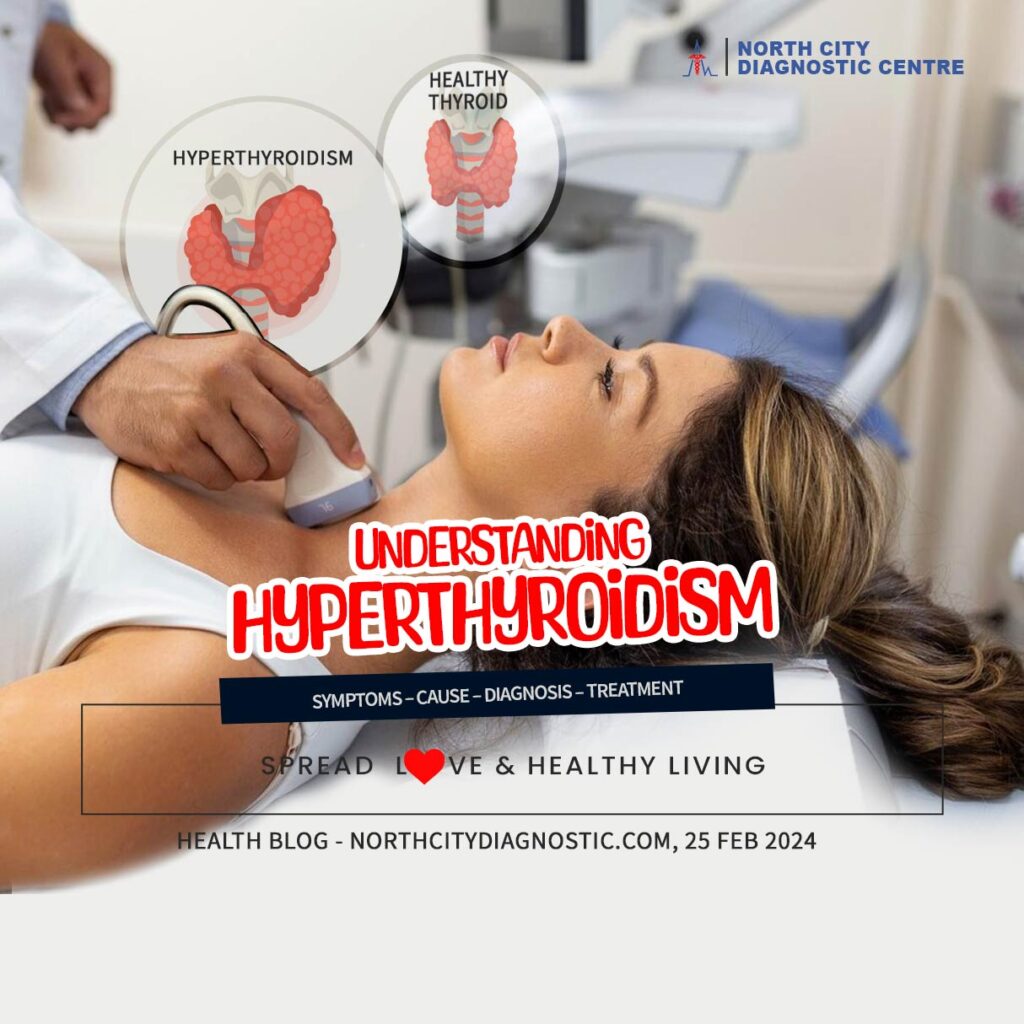
Hyperthyroidism is a medical condition that occurs when the thyroid gland produces an excessive amount of thyroid hormone. The thyroid gland is a small butterfly-shaped organ located in the neck that secretes thyroid hormones. These hormones are essential for the body’s metabolic processes and regulate several vital functions, such as heart rate, body temperature, and weight.
Hyperthyroidism can cause an acceleration in the body’s metabolism, leading to several symptoms such as weight loss, increased appetite, sweating, heat intolerance, fatigue, muscle weakness, hand tremors, and rapid or irregular heartbeat. These symptoms are often distressing and can impact the quality of life.
Fortunately, several treatment options are available for hyperthyroidism. Anti-thyroid medication and radioiodine therapy can be used to slow down the production of hormones by the thyroid gland. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove all or part of the thyroid gland.
It’s essential to note that improvement is possible without medication or other treatment, depending on the underlying cause. Regular follow-up with a healthcare professional is necessary to monitor thyroid hormone levels and ensure that the treatment is effective.
“Losing weight doing nothing isn’t healthy. Check your thyroids.”
Hyperthyroidism can be difficult to diagnose as it may have symptoms similar to other health problems.
Please note the following symptoms associated with an overactive thyroid gland, also known as hyperthyroidism:
Elderly individuals may exhibit symptoms that are not immediately evident, including but not limited to,
These symptoms, if left untreated, may lead to the exacerbation of underlying conditions and should be closely monitored. If you suspect you may have hyperthyroidism or experience any of these symptoms, you should consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment.
Hyperthyroidism has several causes, including,
Iodine is a vital component of T4 and T3 hormones; however, excessive intake of iodine can lead to temporary hyperthyroidism. It is essential to keep track of your iodine intake to avoid any complications. You can find iodine in various foods such as fish and dairy products. It can also be present in medications like cough syrups, contrast dyes, and amiodarone. Be mindful of what you consume to prevent any potential harm.
Thyroiditis is a condition that causes the thyroid gland to swell. It can lead to either too much or too little hormone production, which can be painful or painless. Postpartum thyroiditis occurs within a year of giving birth and can result in the thyroid gland not recovering, leading to hypothyroidism. If you experience any symptoms related to thyroiditis, seek medical attention immediately.
Thyroid nodules can develop on the thyroid gland for unknown reasons. While some nodules produce excess hormones, most are benign and do not pose a threat. However, toxic thyroid nodules can be malignant or cancerous. It is crucial to get a diagnosis through ultrasound or a tissue biopsy called fine needle aspiration to avoid any complications.
Tumors of the ovaries or testes can also cause hyperthyroidism. It is essential to be aware of the symptoms and get a prompt diagnosis to prevent any complications.
High levels of T4 in the blood can be caused by taking certain supplements or excessive amounts of levothyroxine, a thyroid hormone medication. Be mindful of what you consume and consult your doctor before taking any supplements or medications.
Graves’ disease is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system attacks the thyroid gland, causing it to produce excessive thyroid hormones. It is hereditary and more common in people assigned female at birth. Graves’ disease is the most frequent cause of hyperthyroidism, accounting for approximately 85% of cases. If you have a family history of Graves’ disease, consult your doctor to keep any potential risks at bay.
Thyrotoxicosis and hyperthyroidism are two terms that are often used interchangeably in the context of thyroid disorders. However, the two conditions are not the same, and it’s important to understand the difference between them.
Hyperthyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormone. This can be caused by a range of factors, discussed above.
On the other hand, thyrotoxicosis is a more general term that refers to a state of excess thyroid hormone in the body, regardless of the source. The symptoms of thyrotoxicosis can be similar to those of hyperthyroidism, but they can also be more severe, depending on the degree of excess hormone and the duration of the condition. These symptoms can include weight loss, fatigue, irritability, muscle weakness, and heat intolerance.
While hyperthyroidism refers specifically to the overproduction of thyroid hormone by the thyroid gland, thyrotoxicosis is a broader term that encompasses any situation in which there is too much thyroid hormone in the body.
As per data published on Oct 13, 2023, in The Lancet Regional Health, the five-year age standardized relative survival (95% CI) of cervical cancer was 51.7% (50.2%–53.3%).
Five-year Observed Survival percentage as per Population Based Cancer Registries (PBCR) were,
The importance of accurate diagnosis and detection of thyroid abnormalities cannot be overstated. To accomplish this goal, healthcare professionals employ a range of diagnostic tests, including:
The thyroid function tests measure the levels of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) to provide a comprehensive evaluation of thyroid function.
Radioactive iodine uptake test is a vital tool in assessing the thyroid gland’s activity by measuring the amount of radioactive iodine absorbed.
Thyroid ultrasound is a non-invasive diagnostic test utilizes sound waves to create images of the thyroid gland, allowing for the detection of abnormalities such as nodules or enlargement.
Thyroid scan involves the injection of a radioactive tracer into the body, providing detailed images to evaluate thyroid structure and function.
FNAC involves the removal of cells from thyroid nodules for examination under a microscope, enabling healthcare professionals to determine whether they are benign or malignant.
Thyroid Stimulating Immunoglobulin (TSI) assesses the level of thyroid stimulating immunoglobulin in the blood, which is often elevated in Graves’ disease, a common cause of hyperthyroidism.
diagnostic tests are essential in providing a comprehensive evaluation of thyroid function and the detection of any abnormalities. With accurate diagnosis, healthcare professionals can provide patients with appropriate treatment and care, ultimately leading to improved health outcomes.
There is no clear way to prevent hyperthyroidism. But being aware is a critical aspect.
Risk Factors
There are a few things that can increase the chances of developing hyperthyroidism. These include
If you have the risk factors there are few things that you may consider to maintain a healthy thyroid,
If left untreated, hyperthyroidism can have adverse effects on multiple systems in the body. Your heart, bones, and other systems can be affected by an overactive thyroid.
Some common complications associated with untreated or undertreated hyperthyroidism include
Therefore, if you experience any symptoms of hyperthyroidism, it is crucial to schedule an appointment with your healthcare provider. They will examine you thoroughly, provide you with a proper diagnosis, and recommend an appropriate treatment plan.
Hyperthyroidism can be treated in several ways depending on the age, health, and severity of the condition.
Treatment options include anti-thyroid medicine, beta blockers, radioiodine therapy, and thyroidectomy.
Anti-thyroid medicine can relieve symptoms by preventing the thyroid gland from producing too many hormones.
Beta blockers can alleviate symptoms such as a tremor and rapid heart rate.
Radioiodine therapy shrinks the thyroid gland but can lead to hypothyroidism.
Thyroidectomy is surgery to remove part or all of the thyroid gland. All surgeries require lifelong medication to maintain healthy hormone and calcium levels.
At North City Diagnostic Center we offer personalized testing schedule that aligns with your medical history and risk factors. Consistent monitoring can be invaluable for early detection and effective management of arthritis. It’s not just about how often you test but making sure that the tests are aligned with your overall health profile for maximum benefit.
#HyperthyroidismAwareness #ThyroidHealth #KnowYourThyroid #ThyroidDisorder #HyperthyroidSymptoms #ThyroidTreatment #HealthAwareness #ThyroidSupport #NDC #HealthFirst #DiagnosticServices #NorthCityDiagnosticCentre #RoadmapToGoodHealth #Wellbeing #HealthandWellness
35-A ,Canal West Road
Near Gouri Bari Bus Stop
Kolkata – 700004.
Local: +91 33 6605 0888